<p class="article-intro">Acquired mutations detection by the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) is largely used in oncohaematology. Germline mutations have also shown to play a major role in this context and specific panels help identifying the familial forms of leukaemias and/or inherited bone marrow failure syndromes (IBMFS).</p>
<p class="article-content"><div id="keypoints"> <h2>Keypoints</h2> <ul> <li>Haematological malignancies can be sporadic or familial.</li> <li>Recognition of HMM is crucial for appropriate patient management.</li> <li>A genetic diagnosis, although challenging, can be achieved by the use of NGS and other molecular techniques.</li> </ul> </div> <p>The use of molecular technologies, particularly NGS, allowed the identification of germline mutations implicated in familial acute leukaemia, myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and IBMFS. Distinction between the acquired and inherited forms may have important implications for the treatment, management and monitoring of selected patients. Therefore, if hereditary myeloid malignancies (HMM) are suspected, germline genetic analyses may be performed by the use of molecular NGS panels.</p>
<p class="article-intro">Acquired mutations detection by the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) is largely used in oncohaematology. Germline mutations have also shown to play a major role in this context and specific panels help identifying the familial forms of leukaemias and/or inherited bone marrow failure syndromes (IBMFS).</p>
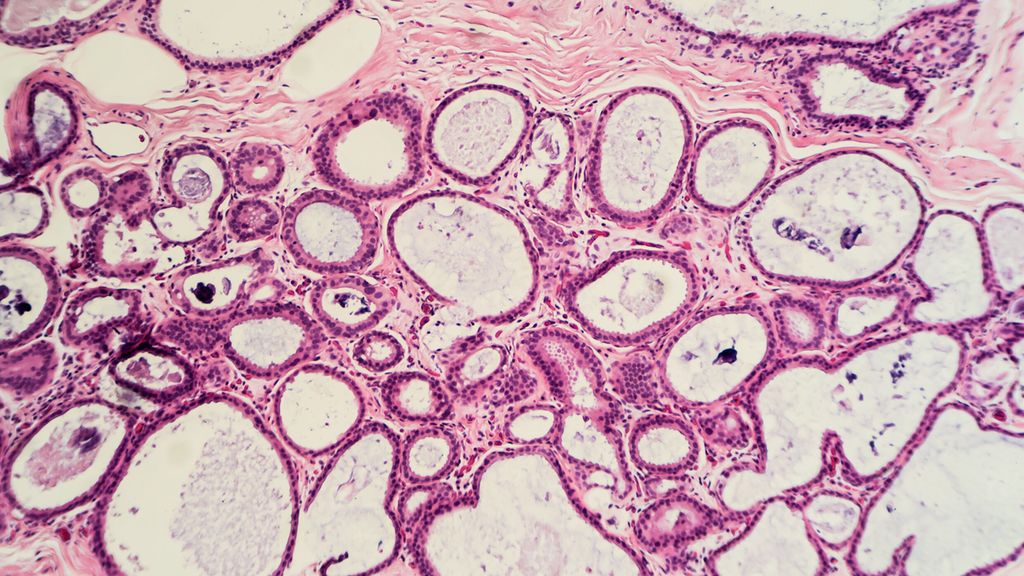
<p class="article-content"><div id="keypoints"> <h2>Keypoints</h2> <ul> <li>Haematological malignancies can be sporadic or familial.</li> <li>Recognition of HMM is crucial for appropriate patient management.</li> <li>A genetic diagnosis, although challenging, can be achieved by the use of NGS and other molecular techniques.</li> </ul> </div> <p>The use of molecular technologies, particularly NGS, allowed the identification of germline mutations implicated in familial acute leukaemia, myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and IBMFS. Distinction between the acquired and inherited forms may have important implications for the treatment, management and monitoring of selected patients. Therefore, if hereditary myeloid malignancies (HMM) are suspected, germline genetic analyses may be performed by the use of molecular NGS panels.</p> <h2>Mutation testing in oncohaematology</h2> <p>In oncohaematology, mutation detection is largely applied due to its crucial role in disease characterisation and evaluation, prediction of prognosis and/or treatment responsiveness. NGS panels are used along with other methodologies by different laboratories in order to allow the identification of acquired mutations associated with the tumour and to help stratifying patients. Although myeloid neoplasms, such as acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) and MDS, mainly occur sporadically, germline mutations associated with predisposition to HMM have been previously described.<sup>1, 2</sup> Concurrently, the advent of NGS enabled the detection of an increasing number of gene mutations associated with HMM: identifying these mutations is crucial in terms of patient management.</p> <h2>HMM: why do we test?</h2> <p>The detection of germline mutations involved in HMM confirms a genetic diagnosis of the disease of interest. Apart from this obvious genetic diagnostic aspect, patient management and follow-up can be significantly modulated accordingly. Since a number of patients with haematological malignancies undergo haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), selection of healthy donors would be an essential procedure. Therefore, in the case when a germline pathogenic mutation is detected in the affected individual considered for HSCT, healthy siblings, who are not carriers of the same mutation, would be required. If a mutation carrier is used as a donor, this might result in failure of stem cell engraftment and donor-derived leukaemia.<sup>1</sup> Moreover, conditioning regimens may be adapted and inappropriate treatments avoided according to the presence of a germline pathogenic variant.<sup>3, 4</sup> Finally yet importantly, the identification of carriers or affected patients allows for providing cancer risk assessments, surveillance and appropriate genetic counselling for both patients and family members.</p> <h2>HMM: whom to test?</h2> <p>The selection of patients who require genetic testing for HMM may be challenging and different strategies may be country/ hospital/case dependent. Nevertheless, previously reported clinical screening algorithms may be used as explanatory examples.<sup>4</sup> Main testing criteria include: a personal and/or family history of haematological malignancies; relatively young age of onset of cancer; the presence of a potential germline mutation implicated in HMM encountered during the acquired mutation test; donor evaluation in the case of HMM organ manifestations, unexplained cytopenia or abnormal bone marrow biopsy.</p> <h2>Testing challenges</h2> <p>Testing for HMM and IBMFS present several challenges both clinically and technically. Firstly, this is a group of extremely heterogeneous disorders. In order to screen for one disease, in fact, multiple genes would normally need to be tested. Furthermore, the phenotypes may be either overlapping between multiple diseases or not as clear as expected: an obvious phenotype-genotype correlation may be absent; the full clinical spectrum of the disorder may not be present; the abnormalities may evolve over time; the age of onset may be highly variable. In addition, some individuals may carry the mutation and be unaffected, whereas their children may carry the same mutation and develop the disease.<br /> Although different genetic testing strategies exist, each approach has several limitations. For instance, testing one gene at a time can be in most of the cases questionable due to the genetic heterogeneity of the disorders and the requirement of longer global turnaround times. Targeted gene panels by NGS is thus the mostly used testing strategy, however, the analysis would still be limited to a specific number of genes. Additionally, copy number alterations (CNAs), which have been already reported in HMM,<sup>8, 9</sup> may not be detectable by all the NGS testing strategy. Whole exome sequencing, therefore, may overcome the heterogeneity issue. However, the testing cost would significantly increase, the coverage and assay sensitivity may be reduced and mutations found in intronic or untranslated regions (UTRs), in which recurrent mutations have been well described in HMM (e. g. mutations in 5’- UTR of the <em>ANKRD26</em> gene (Fig. 1)<sup>5</sup>, cannot be detected (enrichment dependent). Expanded exomes testing, which may achieve a higher sensitivity and include certain intronic regions as well as the UTRs<sup>6, 7</sup>, would be a potential strategy solution, although its feasibility would be strictly restricted to a subset of large reference laboratories with extensive expertise in hereditary haematological disorders. Regardless of the strategy used, the absence of a genetic variant does not exclude a diagnosis of HMM or IBMFS.<br /> Due to the complexity and variability of this group of disorders, a multidisciplinary approach between haematologists, clinical and laboratory geneticists would certainly be highly recommended.</p> <p><img src="/custom/img/files/files_datafiles_data_Zeitungen_2019_Leading Opinions_Onko_1905_Weblinks_lo_onko_s54_fig1_zucca.png" alt="" width="820" height="610" /></p> <h2>Testing strategy at the Oncogenomic laboratory (LOG), CHUV</h2> <p>Due to the importance of HMM, the LOG at the Department of Haematology of the CHUV in Lausanne, has designed a targeted gene panel. This comprises 53 genes covering a variety of HMM and IBMFS, which are tested by NGS technology (Fig. 2). In addition, a panel by MLPA (SALSA MLPA Familial MDS-AML probemix by MRC-Holland) can be offered in order to ensure detection of potential CNAs in the following genes: <em>GATA2, TERC, TERT, CEBPA </em>and<em> RUNX1</em>. If large CNAs need to be excluded in additional genes, a SNP array analysis can also be performed.<br /> The gold standard material to be tested would be DNA derived from cultured fibroblasts from a skin biopsy sample, in order to maximally avoid the presence of DNA derived from hematopoietic cells.<sup>10</sup> Nevertheless, additional sample materials are regarded as acceptable including buccal swabs and blood. A patient signed genetic informed consent, however, must be obtained prior to performing hereditary genetic testing.<br /> Additional information, including the detailed list of genes and the request form, can be found at the LOG website: <a href="http://www.chuv.ch/fr/log">www.chuv.ch/fr/log</a>.</p> <p><img src="/custom/img/files/files_datafiles_data_Zeitungen_2019_Leading Opinions_Onko_1905_Weblinks_lo_onko_s55_fig2_zucca.png" alt="" width="820" height="610" /></p></p>
<p class="article-footer">
<a class="literatur" data-toggle="collapse" href="#collapseLiteratur" aria-expanded="false" aria-controls="collapseLiteratur" >Literatur</a>
<div class="collapse" id="collapseLiteratur">
<p><strong>1</strong> Swerdlow SH et al.: WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Revised 4th edition. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2017 <strong>2</strong> Greenberg PL et al.: J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2017, 15(1): 60-87<strong> 3</strong> Bluteau O et al.: Blood 2018; 131(7): 717-32 <strong>4</strong> Univ of Chicago Hemat Malign Cancer Risk Team: Blood 2016; 128(14): 1800-13 <strong>5</strong> Marconi C et al.: J Hematol Oncol 2017; 10: 18 <strong>6</strong> Patwardhan A et al.: Genome Med 2015; 7(1): 71 <strong>7</strong> Meienberg J et al.: Nucleic Acids Res 2015; 43(11): e76 <strong>8</strong> Cavalcante de Andrade S et al.: Cancer Genet 2018; 222- 223: 32-7 <strong>9</strong> Schlegelberger B, HellerPG: Semin Hematol 2017; 54(2): 75-80 <strong>10</strong> Döhner H et al.: Blood 2017; 129(4): 424-47</p>
</div>
</p>